Decoding the Mechanisms Behind GLP-1 Weight Loss Medications and Appetite Regulation
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists represent a transformative advancement in obesity pharmacotherapy, leveraging intricate neuroendocrine pathways to modulate appetite effectively. Unlike traditional appetite suppressants, GLP-1 medications harness the body’s inherent satiety signaling through targeted receptor activation within the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract, providing a scientifically grounded approach to weight management.
Neurohormonal Pathways: GLP-1’s Sophisticated Appetite Modulation
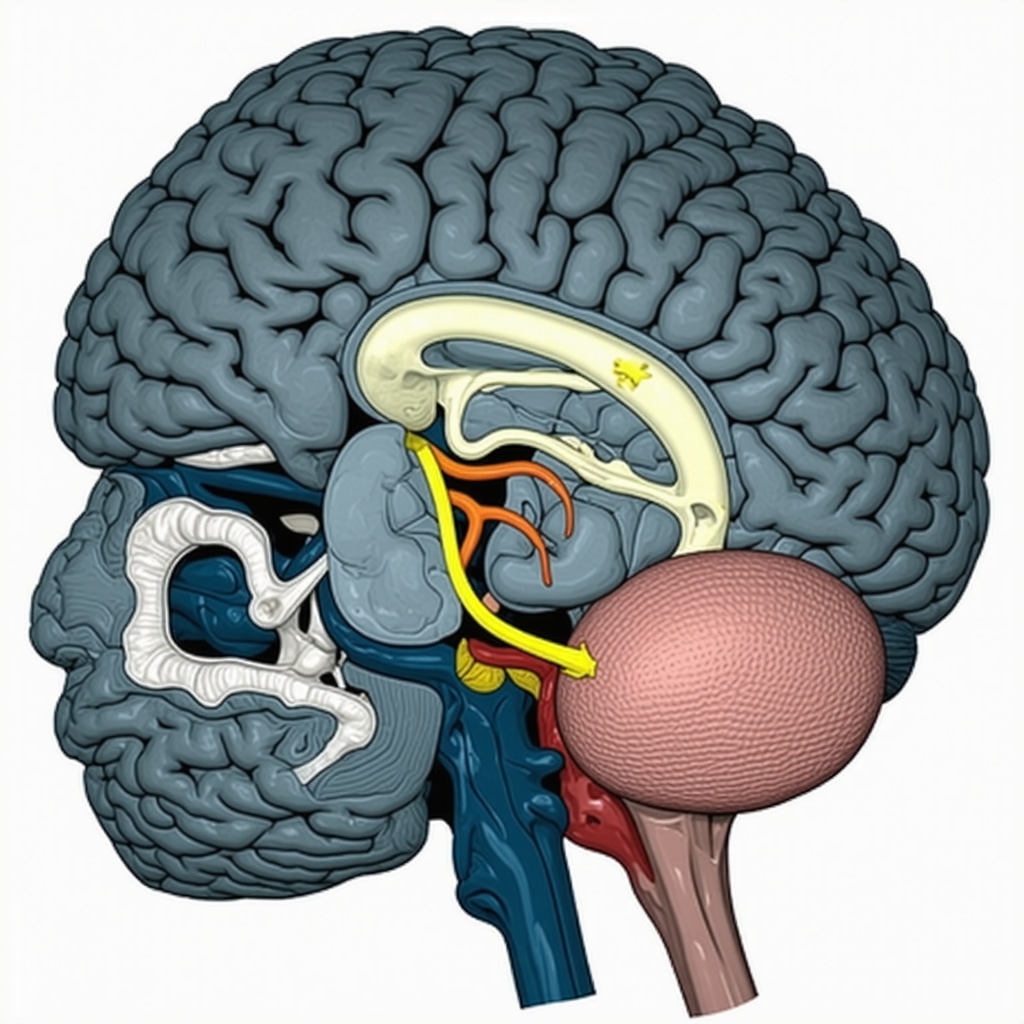
At the core of GLP-1’s efficacy lies its interaction with hypothalamic and brainstem centers responsible for energy homeostasis. GLP-1 receptor agonists stimulate the arcuate nucleus, enhancing pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neuron activity while inhibiting neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neurons, resulting in decreased hunger signals. This dual modulation culminates in reduced caloric intake and improved satiety, as substantiated by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies demonstrating altered activity in appetite-related brain regions during GLP-1 therapy.
How Do GLP-1 Weight Loss Medications Differ from Other Appetite Suppressants in Clinical Practice?
Unlike catecholamine-releasing agents or serotonergic drugs, GLP-1 receptor agonists provide a physiological mimicry of endogenous incretin hormones, minimizing adverse central nervous system effects such as anxiety or insomnia. The prolonged half-life of synthetic analogs like semaglutide allows sustained receptor engagement, facilitating consistent appetite control without the peaks and troughs that compromise efficacy. Clinically, this translates to superior patient adherence and significant, durable weight reduction, as documented in randomized controlled trials published in journals such as The New England Journal of Medicine.
Integrating GLP-1 Therapies into Comprehensive Obesity Management
Effective appetite control via GLP-1 agonists is optimized when combined with physician-guided nutritional counseling and behavioral interventions. This integrative strategy addresses the multifactorial etiology of obesity, enhancing metabolic outcomes beyond isolated pharmacologic effects. For patients interested in exploring these advanced medical options, resources such as our doctor-led fat loss plans offer personalized pathways to sustainable weight management.
Emerging Research and Future Directions in GLP-1 Mediated Appetite Control
Ongoing investigations are elucidating the potential synergistic effects of dual agonists targeting both GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors, aiming to amplify appetite suppression and metabolic benefits. These developments herald a new paradigm in obesity pharmacotherapy, expanding the therapeutic arsenal with enhanced efficacy profiles. Interested professionals are encouraged to review comparative analyses such as semaglutide vs tirzepatide to understand nuanced differences in mechanism and clinical outcomes.
Explore further expert-level insights and share your clinical experiences with GLP-1 weight loss medications by visiting our contact page.
Exploring GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Beyond Appetite Suppression: Metabolic and Cardiovascular Dimensions
While the primary focus of GLP-1 receptor agonists has been appetite regulation and weight loss, accumulating evidence highlights their broader metabolic and cardiovascular benefits. These agents improve glycemic control by enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release in a glucose-dependent manner, thereby reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. Additionally, GLP-1 therapies have demonstrated favorable effects on lipid profiles and blood pressure, contributing to cardiovascular risk mitigation in obese patients with comorbidities.
Clinical trials such as the LEADER and SUSTAIN-6 studies underscore the cardioprotective potential of GLP-1 analogs, positioning them as a dual-purpose intervention for obesity and related metabolic disorders. This multifaceted impact expands the therapeutic appeal of GLP-1 medications within comprehensive obesity management frameworks.
Pharmacokinetic Innovations: Long-Acting Formulations and Patient Adherence
Recent advancements in GLP-1 medication formulations emphasize extended half-lives and improved delivery systems, which enhance patient adherence and treatment satisfaction. Agents like semaglutide and tirzepatide utilize molecular modifications that resist enzymatic degradation, allowing once-weekly dosing regimens. Such pharmacokinetic profiles not only maintain steady receptor activation but also reduce treatment burden, a critical factor in chronic weight management.
What Are the Clinical Implications of Combining GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Agonism in Emerging Therapies?
Dual agonists targeting both GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors represent an innovative frontier in obesity pharmacotherapy. Tirzepatide, for example, leverages this dual mechanism to potentiate appetite suppression and enhance insulin sensitivity. By simultaneously activating two incretin pathways, these therapies may achieve superior weight loss outcomes and metabolic improvements compared to GLP-1 monotherapy.
However, the long-term safety profile and optimal patient selection criteria remain active areas of research. Experts suggest that integrating such dual agonists into personalized treatment plans requires careful consideration of individual metabolic status and comorbid conditions, as outlined in recent consensus guidelines (American Heart Association, 2023).
Practical Considerations: Tailoring GLP-1 Therapy Within Multimodal Weight Loss Programs
Optimal outcomes with GLP-1 medications arise from a holistic approach encompassing lifestyle modification, psychosocial support, and pharmacotherapy. Physicians are encouraged to develop individualized protocols that address behavioral patterns, dietary habits, and exercise capacity. Incorporating telemedicine platforms can facilitate ongoing monitoring and dose adjustments, improving accessibility and patient engagement, as discussed in our article on telemedicine weight loss treatment.
Furthermore, understanding the pharmacodynamics of GLP-1 agents enables clinicians to anticipate and manage common adverse effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, thereby maintaining adherence and minimizing discontinuation rates.
We invite healthcare professionals and patients alike to share their experiences and strategies for maximizing GLP-1 therapy effectiveness by visiting our contact page. Stay updated on the latest developments by exploring our comprehensive resources on FDA-approved weight loss treatments and innovative pharmacological options.

Unraveling the Neuropharmacology Behind GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Basic Appetite Suppression
GLP-1 receptor agonists extend their influence beyond mere appetite suppression by intricately modulating central and peripheral neuropharmacological pathways. Recent neuroimaging and electrophysiological studies reveal that these agents recalibrate reward circuitry in the mesolimbic system, particularly attenuating the dopaminergic response to highly palatable foods. This modulation reduces hedonic eating, a critical driver of obesity in modern obesogenic environments. Moreover, GLP-1 analogs influence vagal afferent signaling, which integrates peripheral satiety signals with central appetite control centers, creating a feedback loop that enhances meal termination signaling.
Such multifaceted neural engagement explains the sustained efficacy of GLP-1 therapies, distinguishing them from traditional anorectics that often evoke tolerance or rebound hyperphagia. These discoveries underscore the importance of considering neuropharmacological mechanisms when designing personalized obesity treatments, especially for patients exhibiting compulsive or reward-driven eating behaviors.
How Does GLP-1 Influence the Brain’s Reward System to Mitigate Overeating? A Closer Look at Dopaminergic Pathways
GLP-1 receptor activation in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and nucleus accumbens modulates dopamine neurotransmission, effectively reducing the reinforcing properties of food stimuli. This neuromodulation dampens the motivational drive to consume calorie-dense foods, thus contributing to decreased spontaneous food intake. Functional MRI studies corroborate these findings by demonstrating reduced activation in reward-related brain regions during GLP-1 therapy, which correlates with improved weight loss outcomes (Neuron, 2021).
Dual and Triple Agonists: The Future of Incretin-Based Therapies in Obesity and Metabolic Disease
Building upon the success of GLP-1 receptor agonists, next-generation pharmacotherapies are exploring polyagonism—targeting multiple receptors simultaneously to harness synergistic metabolic effects. Tirzepatide, the dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist, exemplifies this approach by combining appetite suppression with enhanced insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. Early-phase clinical trials indicate that triple agonists, which also target glucagon receptors, may further potentiate energy expenditure and promote greater weight loss beyond what is achievable with monotherapy.
These polyagonists operate through complex receptor crosstalk and downstream signaling cascades that recalibrate whole-body metabolism. Notably, engagement of glucagon receptors may increase thermogenesis and lipid oxidation, counterbalancing the anabolic effects of insulin and improving metabolic flexibility. However, balancing efficacy with tolerability remains a clinical challenge, as glucagon receptor activation can precipitate gastrointestinal side effects and requires careful dose titration.
Integrating GLP-1 Therapies into Precision Medicine: Tailoring Treatment Based on Patient Phenotypes and Biomarkers
The heterogeneity of obesity pathophysiology necessitates precision medicine approaches to maximize therapeutic efficacy. Biomarker-driven stratification, including genetic variants influencing incretin receptor expression and metabolic profiles, can inform GLP-1 therapy candidacy and dosing strategies. For instance, patients with predominant insulin resistance may benefit more from dual agonists targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, whereas those with significant hedonic eating behaviors might respond preferentially to agents with pronounced central nervous system penetration.
Emerging technologies such as continuous glucose monitoring and digital phenotyping enable real-time assessment of metabolic responses and behavioral patterns, facilitating dynamic adjustment of pharmacotherapy. This paradigm shift from one-size-fits-all to individualized regimens optimizes weight loss outcomes and minimizes adverse events, aligning with contemporary clinical guidelines emphasizing personalized obesity care (Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2021).
Advanced Clinical Strategies: Combining GLP-1 Agonists with Behavioral and Nutritional Interventions for Sustainable Weight Loss
GLP-1 receptor agonists achieve their full potential when integrated within comprehensive weight management programs that address behavioral, psychological, and nutritional dimensions. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) tailored to modulate eating behaviors synergizes with pharmacological appetite control, addressing underlying triggers of overeating. Nutritional counseling emphasizing low glycemic index foods complements GLP-1-induced satiety enhancement, fostering healthier eating patterns.
Moreover, structured physical activity protocols enhance metabolic rate and insulin sensitivity, further amplifying the benefits of GLP-1 therapies. Telehealth platforms and digital apps provide scalable solutions for continuous patient engagement, remote monitoring, and tailored support, crucial for long-term adherence and relapse prevention.
Healthcare providers and patients seeking to explore these advanced, multimodal approaches can access detailed expert guidance and personalized plans via our doctor-led fat loss plans. Engage with our community to share insights and optimize your therapeutic journey.
Deciphering GLP-1’s Influence on Dopaminergic Reward Circuitry: A Neuropharmacological Perspective
Beyond traditional appetite suppression, GLP-1 receptor agonists intricately modulate the brain’s reward pathways, particularly targeting the mesolimbic dopaminergic system. This neuromodulation attenuates the hedonic drive for calorie-dense foods by diminishing dopamine release in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and nucleus accumbens, which are pivotal nodes in reward processing. Such targeted action reduces compulsive eating behaviors often resistant to lifestyle interventions and contributes to sustained weight loss efficacy.
Can Modulation of GLP-1 Receptors Alter Food Reward Sensitivity in Obese Patients?
Clinical neuroimaging studies have demonstrated that GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce activation in reward-related brain regions when patients are exposed to high-calorie food cues, effectively lowering food craving intensity. This mechanism differs fundamentally from conventional appetite suppressants and offers promising therapeutic potential for patients with reward-driven overeating. For an in-depth discussion, see the comprehensive review in Neuron, 2021.
Polyagonist Therapies: Harnessing Synergistic Metabolic Pathways for Enhanced Weight Loss
Emerging pharmacological innovations are focusing on dual and triple incretin receptor agonists that simultaneously target GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors. These agents exploit complementary signaling cascades to amplify anorectic effects, improve insulin sensitivity, and increase energy expenditure via augmented thermogenesis. Tirzepatide exemplifies this approach, delivering superior weight loss and glycemic control compared to GLP-1 monotherapy, as evidenced by recent phase III trial data.
Precision Medicine in Obesity Pharmacotherapy: Biomarkers and Phenotype-Driven Treatment Optimization
Given the heterogeneity of obesity phenotypes, integrating genetic, metabolic, and behavioral biomarkers into clinical decision-making enhances therapeutic responsiveness and minimizes adverse effects. For example, patients exhibiting predominant insulin resistance may derive greater benefit from dual GLP-1/GIP agonists, while those with hyperphagic or hedonic eating profiles might require agents with enhanced central nervous system penetration. Advances in digital phenotyping and continuous monitoring technologies enable real-time therapy adjustments, facilitating a dynamic and bespoke treatment paradigm. The role of personalized medicine in incretin therapies is extensively reviewed in Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2021.
Integrative Strategies: Combining Pharmacotherapy with Behavioral and Nutritional Interventions for Long-Term Success
Maximizing the therapeutic impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists necessitates embedding pharmacologic treatment within comprehensive behavioral health frameworks. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) targeting maladaptive eating patterns, alongside tailored nutritional guidance emphasizing glycemic control, synergize with GLP-1 induced satiety mechanisms. Incorporating physical activity enhances metabolic conditioning and insulin sensitivity, while telemedicine platforms facilitate ongoing patient engagement and adherence monitoring, critical for mitigating relapse. Our doctor-led fat loss plans exemplify this integrative approach, offering personalized, evidence-based pathways to sustainable weight loss.
Healthcare professionals and patients seeking to harness these advanced insights are encouraged to connect with our expert team via our contact page, ensuring access to cutting-edge, individualized obesity treatment strategies.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Nuanced Neuropharmacological Targeting Enhances Long-Term Appetite Control
GLP-1 receptor agonists uniquely recalibrate central appetite and reward circuits, particularly within the mesolimbic dopamine pathway, which is critical for mitigating hedonic overeating. This neuropharmacological precision distinguishes GLP-1 therapies from conventional anorectics prone to tolerance and rebound effects, supporting sustained weight loss in clinical practice.
Synergistic Polyagonism Represents the Next Frontier in Metabolic Regulation
Emerging dual and triple incretin receptor agonists, such as tirzepatide, integrate GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor modulation to deliver complementary metabolic benefits including enhanced insulin sensitivity, appetite suppression, and increased energy expenditure. These agents herald a paradigm shift in obesity pharmacotherapy by expanding beyond mono-receptor targeting.
Precision Medicine and Digital Phenotyping Optimize Therapeutic Outcomes
Stratifying patients by genetic, metabolic, and behavioral phenotypes allows for tailored incretin-based treatment regimens. Integrating continuous glucose monitoring and digital behavioral assessments facilitates real-time pharmacotherapy adjustments, maximizing efficacy while minimizing adverse events, and aligning with modern personalized obesity care frameworks.
Integrative Multimodal Approaches Amplify GLP-1 Medication Effectiveness
Combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with evidence-based behavioral interventions, nutritional counseling, and structured physical activity yields synergistic benefits, reinforcing sustainable lifestyle change. Telemedicine platforms further enhance adherence and accessibility, critical components in chronic obesity management.
Pharmacokinetic Innovations Improve Patient Adherence and Treatment Consistency
Long-acting formulations of GLP-1 agonists with molecular modifications extend half-lives and reduce administration frequency. These advances minimize pharmacodynamic fluctuations, enhancing tolerability and patient compliance, which are vital for achieving durable weight loss results.
Curated Expert Resources
1. “Neuron” (2021) – Neuropharmacology of GLP-1 Receptors: This peer-reviewed journal article provides in-depth neuroimaging and electrophysiological evidence demonstrating GLP-1’s modulation of dopaminergic reward circuits, essential for understanding appetite regulation beyond simple satiety mechanisms.
2. “Nature Reviews Endocrinology” (2021) – Precision Medicine in Obesity: A comprehensive review addressing biomarker-driven treatment stratification and digital phenotyping in incretin-based therapies, offering critical insights for tailoring GLP-1 pharmacotherapy.
3. The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) – Semaglutide Clinical Trials: Landmark randomized controlled trials elucidating the efficacy, safety, and long-term outcomes of GLP-1 receptor agonists in weight management, serving as clinical evidence standards.
4. American Heart Association (2023) Consensus Guidelines: Authoritative guidance on integrating dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists into metabolic and cardiovascular risk reduction strategies, highlighting clinical considerations for emerging therapies.
5. LossWeight4All Doctor-Led Fat Loss Plans: Expert-curated, personalized medical weight loss programs that incorporate GLP-1 therapies alongside behavioral and nutritional strategies, accessible at Doctor-Led Fat Loss Plans.
Final Expert Perspective
GLP-1 weight loss medications have redefined obesity treatment by intricately engaging neuroendocrine and reward pathways to achieve potent appetite regulation. The evolution toward polyagonist therapies and precision medicine underscores a future where treatment is both biologically sophisticated and individually tailored. Integrative strategies that combine pharmacotherapy with behavioral and nutritional interventions optimize patient outcomes and support sustainable fat loss. For clinicians and patients committed to advancing beyond traditional approaches, exploring comprehensive resources like our doctor-led fat loss plans and comparative analyses such as the semaglutide vs tirzepatide guide will provide critical insights for informed decision-making. Engage with our expert team via the contact page to deepen your understanding and optimize your clinical or personal therapeutic journey.
